Uric Acid : A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Managing Impact
Uric acid is a natural substance in the human body, but its balance is critical for maintaining overall health. Excessive or deficient levels can lead to a arrange of health concerns. This articles dives into what uric acid is, its role in the body, the consequence of imbalance and strategies for managing levels effectively.
What is Uric Acid ?
Uric acid is a waste product that forms when the body breaks down purines, compounds found naturally in the body and in certain foods. Once produced, uric acid dissolves int he blood and is transported to the kidneys, where it is excreted through urine. In healthy individuals, this process keeps uric acid levels within a normal range.
Purines are present in many food, particularly in high-protein sources such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood. Some beverages, including beer and sugary drinks, are also significant sources of purines.
Normal Uric Acid Levels
Maintaining balanced uric acid levels is essential for preventing health issues. The typical reference ranges for serum uric acid levels are :
- Men : 3.4 to 7.0 mg/dl
- Women : 2.4 to 6.0 mg/dl
- Children : 2.0 to 5.5 mg/dl
However, these values may very slightly depending on the laboratory performing the test. Routine blood tests can determine whether an individual’s levels fall within these ranges.
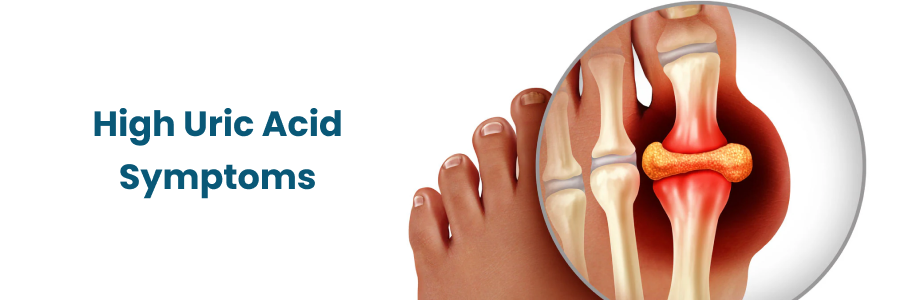
High Uric Acid (Hyperuricemia)
Hyperuricemia occurs when uric acid levels exceed the normal range. while it may not always cause symptoms , sustained high levels can lead to complications , including :
1. Gout :
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joint. It often results in sudden, intense pain , redness and swelling , frequently in the big toe.
2. Kidney Stones :
Excess uric acid can crystallized in the kidneys, forming painful kidney stones that may require medical intervention.
3. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) :
Persistency high uric acid levels can damage the kidneys over time, impairing their ability to filter waste effectively.
Causes Of Hyperuricemia
- Dietary Factors : high intake of purine-rich foods, alcohol and fructose.
- Health Conditions : Obesity, diabetes, hypertension and metabolic syndrome.
- Medications : Certain diuretics and medications used for treating high blood pressure.
- Genetics : Family history of gout or kidney stone can increase the risk.
Low Uric Acid Levels (Hypouri
Although less common, hypouricemia- abnormally low uric acid levels – can also pose health risks. Causes may include :
- Liver Disease : Reduced production of uric acid.
- Fanconi Syndromes : A rare kidney disorder that leads to excessive loss of uric acid.
- Medications : Drugs like allopurinol, often used to treat gout, can lower uric acid levels excessively.
While hypouricemia is typically asymptomatic, it may indicate an underlying condition requiring medical evaluation.
Managing Uric Acid Levels
Whether you’re aiming to lower high uric acid or maintain a healhty balance, lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions can help.
1. Dietary Adjustments –
Reduce purine-rich Foods : Avoid or limit foods like red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain fish (e.g., anchovies, sardines)
Increase Low-purine Foods : Incorporate vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy, and cherries. Cherries and cherry juice, in particular, are known to help reduce uric acid levels.
Limit Alcohol and sugary Drinks : Alcohol, especially beer, and fructose-rich drinks can raise uric levels signifiacntly.
2. Stay Hydrated –
Drinking plenty of water helps the kidneys flush out excess uric acid. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, more if you are active or in a hot climate.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight –
Excess body weight increases uric acid production and reduces its excretion. Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise can improve levels.
4. Medications –
In case where lifestyle changes are insufficient, medications may be necessary.
These include :
Allopurinol : Reduces uric acid production.
5. Regular Monitoring
Periodic blood tests can help track uric acid levels and assess the effectiveness of dietary or medical interventions.
Interesting Facts About Uric Acid
- Protective Role : Uric acid acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage. However, excessive levels can have the opposite effect.
- Disease of Kings : Historically, gout was called the “disease of kings” due to its association with rich diets with alcohol consumption.
- Diurnal Variations : Uric acid levels fluctuate throughout the day, often peaking in the morning.
- Evolutionary Insight : Unlike most mammals, humans lake the enzyme uricase, which breaks down uric acid. This may have provided evolutionary advantages, such as enhanced brain function.
When to See a Doctor ?
Persistence symptoms like joint pain, swelling or frequent kidney stones warrant medical attention. Consulting a a healthcare provider ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, especially for underlying conditions contributing to abnormal uric acid levels.
Conclusion
Uric acid is a small but significant player in overall health. while it serves a protective role as an antioxidant , imbalances-whether too high or too low-can lead to serious health issues. By understanding the causes and effects of abnormal uric acid levels and adopting prevention measures like dietary adjustments, hydration and regular monitoring, individuals can maintain optimal levels and support long-term health. If symptoms persist, seeking professional medical advice is crucial for effective management.
